Si joint x ray oblique – Prepare to delve into the enigmatic realm of sacroiliac joint anatomy, where oblique x-ray views hold the key to unlocking its hidden secrets. As we embark on this journey, let us unravel the intricacies of this pivotal joint, its surrounding structures, and the profound insights offered by oblique x-ray imaging.
Beyond mere anatomical exploration, we will venture into the realm of diagnostic features, uncovering the telltale signs that illuminate sacroiliac joint disorders. Join us as we decipher the cryptic language of oblique x-rays, revealing the criteria that guide interpretation and reporting.
Sacroiliac Joint Anatomy
The sacroiliac (SI) joint is a strong, synovial joint located between the sacrum and the ilium, which is the largest bone of the pelvis. It is a crucial weight-bearing joint that transmits forces between the spine and the lower extremities.
The SI joint is formed by the auricular surfaces of the sacrum and the ilium. The auricular surfaces are covered with a thin layer of cartilage, which provides a smooth surface for movement. The joint is surrounded by a number of ligaments, including the anterior sacroiliac ligament, the posterior sacroiliac ligament, and the interosseous sacroiliac ligament.
These ligaments help to stabilize the joint and prevent excessive movement.
The SI joint is also surrounded by a number of muscles, including the gluteus maximus, the gluteus medius, and the piriformis. These muscles help to control movement of the joint and provide stability.
Surrounding Bones, Si joint x ray oblique
The SI joint is formed by the sacrum and the ilium. The sacrum is a triangular bone located at the base of the spine. It is composed of five fused vertebrae. The ilium is the largest bone of the pelvis.
It forms the lateral and anterior walls of the pelvis.
Surrounding Ligaments
The SI joint is surrounded by a number of ligaments, including the anterior sacroiliac ligament, the posterior sacroiliac ligament, and the interosseous sacroiliac ligament.
Si joint x ray oblique is a diagnostic imaging technique that helps to visualize the sacroiliac joint. This joint is located between the pelvis and the spine, and it can be a source of pain and discomfort. If you are experiencing pain in your lower back or pelvis, your doctor may recommend a si joint x ray oblique to help determine the cause.
If you are planning a hunting trip in New Mexico, be sure to check out new mexico unit 36 elk for information on hunting regulations and tips. After your hunting trip, if you experience any pain in your lower back or pelvis, be sure to see your doctor and ask about a si joint x ray oblique.
- The anterior sacroiliac ligament is a thick, fibrous ligament that runs from the anterior surface of the sacrum to the anterior surface of the ilium.
- The posterior sacroiliac ligament is a thick, fibrous ligament that runs from the posterior surface of the sacrum to the posterior surface of the ilium.
- The interosseous sacroiliac ligament is a thin, fibrous ligament that runs between the sacrum and the ilium.
Surrounding Muscles
The SI joint is surrounded by a number of muscles, including the gluteus maximus, the gluteus medius, and the piriformis.
- The gluteus maximus is a large, powerful muscle that covers the buttocks. It extends from the sacrum and the ilium to the femur.
- The gluteus medius is a thick, triangular muscle that lies deep to the gluteus maximus. It extends from the ilium to the femur.
- The piriformis is a small, pear-shaped muscle that lies deep to the gluteus medius. It extends from the sacrum to the femur.
Oblique X-Ray Views
Oblique x-ray views are crucial in assessing the sacroiliac joint, providing unique perspectives not captured by anteroposterior views.
Oblique views are taken at an angle to the joint, allowing for visualization of the joint surfaces in different planes. This helps in identifying abnormalities or changes in the joint structure that may not be visible on anteroposterior views alone.
Interpretation of Oblique Views
- Anterior Oblique View:This view shows the joint from the front and slightly to the side. It allows for assessment of the anterior aspect of the joint, including the iliac and sacral articular surfaces, as well as the anterior sacroiliac ligaments.
- Posterior Oblique View:This view shows the joint from the back and slightly to the side. It provides visualization of the posterior aspect of the joint, including the posterior sacroiliac ligaments and the relationship between the sacrum and ilium.
Diagnostic Features
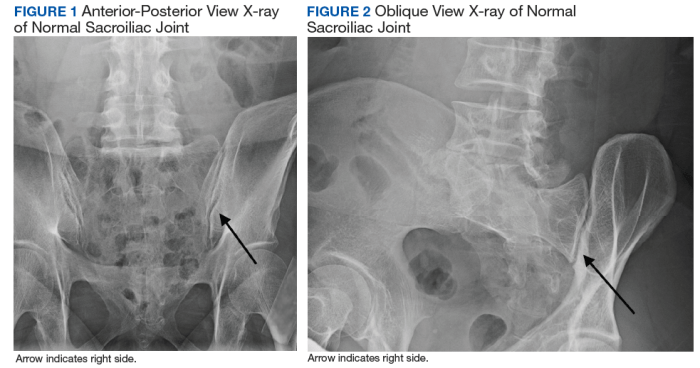
Oblique x-rays of the sacroiliac joint provide valuable information for diagnosing disorders affecting this joint. Key diagnostic features include:
Subluxation:Displacement of the sacrum relative to the ilium, indicating instability or ligamentous injury.
Sclerosis:Increased bone density, often seen in degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis.
Erosions:Areas of bone loss, indicative of inflammatory processes like ankylosing spondylitis.
Ankylosis:Fusion of the sacroiliac joint, resulting in loss of mobility.
Signs and Symptoms of Sacroiliac Joint Disorders
Patients with sacroiliac joint disorders may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Low back pain that radiates to the buttocks or legs
- Pain that worsens with prolonged sitting or standing
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion in the lower back
- Tenderness over the sacroiliac joint
Interpretation and Reporting: Si Joint X Ray Oblique
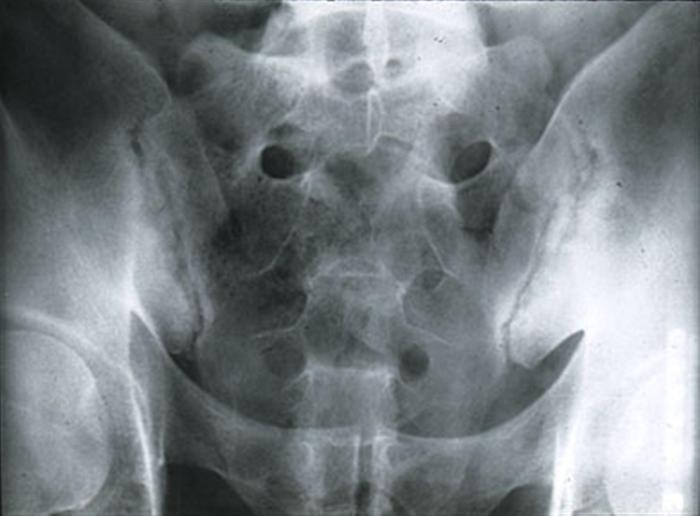
Interpretation of oblique x-rays of the sacroiliac joint involves assessing joint alignment, symmetry, and any abnormalities. These x-rays provide valuable information about the joint’s structure and can aid in diagnosing conditions affecting it.
Assessment Criteria
The following criteria are used to assess oblique x-rays of the sacroiliac joint:
- Joint Alignment:The joint should be aligned in a relatively straight line, with the sacrum and ilium meeting at a smooth and congruent surface.
- Symmetry:The joint should be symmetrical on both sides, with similar appearances and dimensions.
- Abnormalities:Any deviations from normal alignment, symmetry, or the presence of any lesions, erosions, or sclerosis should be noted.
Interpretation
Based on the assessment criteria, oblique x-rays of the sacroiliac joint can be interpreted as follows:
- Normal:The joint is aligned, symmetrical, and free of any abnormalities.
- Abnormal:Deviations from normal alignment, symmetry, or the presence of abnormalities may indicate underlying conditions, such as sacroiliitis, osteoarthritis, or other joint disorders.
Differential Diagnoses
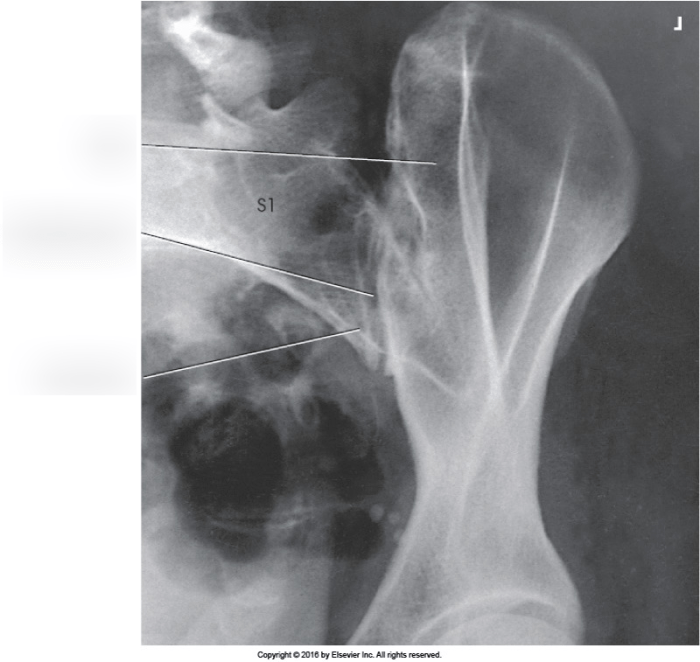
Oblique x-rays of the sacroiliac joint can reveal a variety of abnormalities, including inflammation, erosion, and sclerosis. These findings can be indicative of several conditions, including sacroiliitis, osteoarthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
Sacroiliitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the sacroiliac joint. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including infection, trauma, and autoimmune disorders. Oblique x-rays of the sacroiliac joint may show evidence of inflammation, such as swelling and tenderness.
The si joint x ray oblique provides detailed images of the sacroiliac joint, which can be useful for diagnosing conditions like sacroiliitis. But if you’re looking for a fun distraction while waiting for your results, why not take the nerd or mean girl quiz ? Find out if you’re more like Hermione Granger or Regina George! And when you’re done, don’t forget to follow up with your doctor to discuss your si joint x ray oblique results.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that can affect the sacroiliac joint. It is caused by the breakdown of cartilage, which leads to pain, stiffness, and swelling. Oblique x-rays of the sacroiliac joint may show evidence of osteoarthritis, such as narrowing of the joint space and the presence of osteophytes.
Ankylosing spondylitis is an autoimmune disorder that can affect the sacroiliac joint. It is characterized by inflammation and fusion of the vertebrae. Oblique x-rays of the sacroiliac joint may show evidence of ankylosing spondylitis, such as sacroiliitis and the presence of syndesmophytes.
Comparison of Imaging Features
The imaging features of sacroiliac joint disorders can be compared and contrasted to help differentiate between these conditions. For example, sacroiliitis is typically characterized by inflammation and swelling, while osteoarthritis is characterized by narrowing of the joint space and the presence of osteophytes.
Ankylosing spondylitis is characterized by inflammation and fusion of the vertebrae.
By comparing and contrasting the imaging features of sacroiliac joint disorders, it is possible to make a more accurate diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Clinical Implications
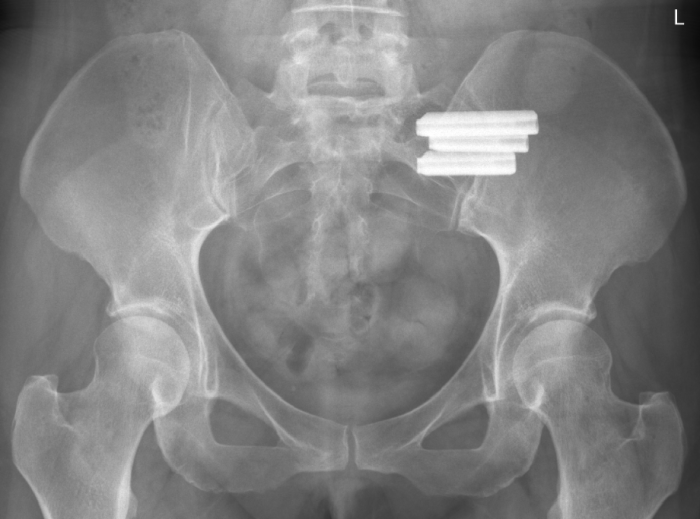
Oblique x-rays of the sacroiliac joint provide valuable information that can guide treatment decisions and patient management.
If you’re dealing with SI joint pain, you might have an SI joint X-ray oblique. This is a special type of X-ray that can help your doctor see the joint from different angles. Did you know that the Queen of the South is a popular TV show about drug trafficking? Anyway, back to your SI joint X-ray oblique.
It can help your doctor diagnose the cause of your pain and recommend the best treatment plan.
The findings on these x-rays can help identify the underlying cause of sacroiliac joint pain and guide appropriate treatment options.
Treatment Decisions
- Conservative Treatment:If the x-rays show no significant abnormalities, conservative treatment options such as physical therapy, pain medication, and lifestyle modifications may be recommended.
- Injections:In some cases, injections of corticosteroids or other medications may be used to reduce inflammation and pain in the sacroiliac joint.
- Surgery:In severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be considered to stabilize or fuse the sacroiliac joint.
Patient Management
- Activity Modification:Patients may be advised to modify their activities to avoid aggravating the sacroiliac joint pain.
- Posture Correction:Physical therapy can help improve posture and reduce stress on the sacroiliac joint.
- Weight Management:Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce pressure on the sacroiliac joint.
Additional Imaging Modalities
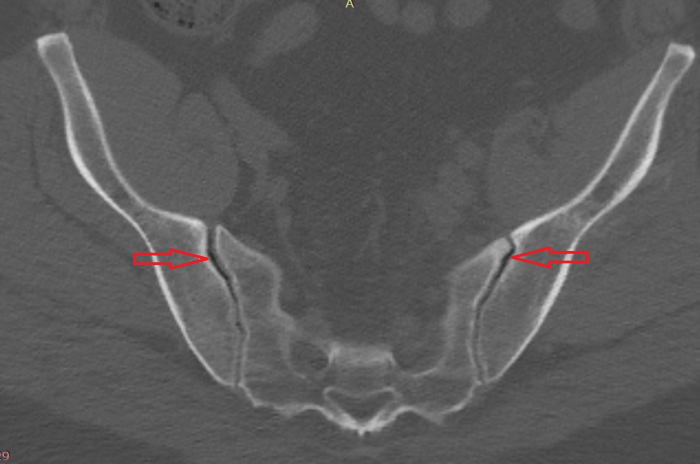
While plain radiography provides a useful initial assessment of the sacroiliac joint, advanced imaging modalities like computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offer more detailed information.
CT scans excel in visualizing bony structures, including the sacroiliac joint and surrounding vertebrae. They can detect subtle fractures, sclerosis, and erosions that may not be apparent on X-rays. However, CT scans have limited soft tissue contrast, making them less effective for evaluating ligamentous injuries or inflammatory changes.
MRI, on the other hand, excels in visualizing soft tissues. It can clearly depict the sacroiliac ligaments, muscles, and nerves, allowing for the assessment of ligamentous tears, muscle strains, and nerve entrapment. MRI also provides excellent contrast between different tissues, making it useful for identifying inflammatory changes and differentiating between various pathologies.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- X-ray:Cost-effective, widely available, provides a good overview of bony structures, but limited soft tissue visualization.
- CT:Detailed bony visualization, can detect subtle fractures and erosions, but limited soft tissue contrast.
- MRI:Excellent soft tissue visualization, can assess ligaments, muscles, and nerves, but more expensive and less widely available.
Key Questions Answered
What is the purpose of an oblique x-ray view of the sacroiliac joint?
Oblique x-ray views provide unique perspectives of the sacroiliac joint, allowing for better visualization of its alignment and potential abnormalities.
What are the key diagnostic features visible on oblique x-rays of the sacroiliac joint?
Key diagnostic features include joint alignment, symmetry, subluxation, sclerosis, and erosions, which can indicate various sacroiliac joint disorders.
How can oblique x-rays help in diagnosing sacroiliac joint disorders?
Oblique x-rays can help identify and differentiate between different sacroiliac joint disorders, such as sacroiliitis, ankylosing spondylitis, and osteoarthritis.