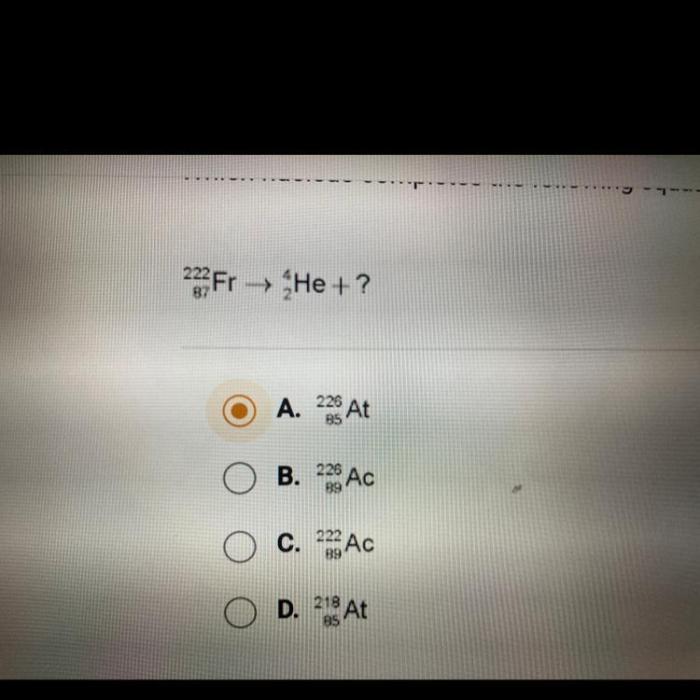
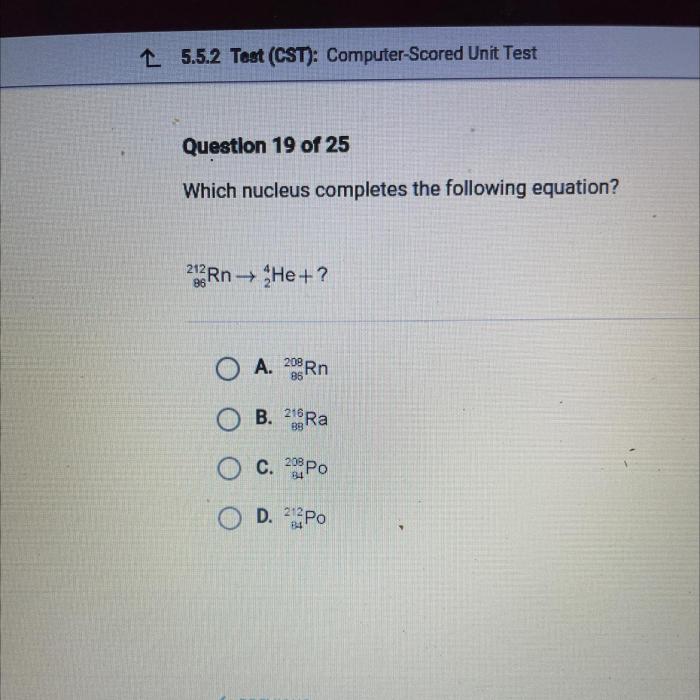
In the realm of chemistry, equation completion plays a pivotal role, providing a structured approach to understanding and predicting the outcome of chemical reactions. At the heart of this process lies the question: which nucleus completes the following equation? This inquiry invites us to delve into the fascinating world of nuclear chemistry, where the properties and behavior of different nuclei dictate the course of chemical transformations.
The concept of equation completion hinges on the ability to identify the missing reactant or product in a chemical equation. This requires a thorough understanding of the elements involved, their atomic structures, and the fundamental principles governing chemical reactions. By systematically considering the various nuclei that can participate in a given equation, we can deduce the most probable completion.
Equation Completion: Which Nucleus Completes The Following Equation

Equation completion is the process of balancing chemical equations by adding coefficients to the reactants and products. This ensures that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. The most common equations that require completion are redox reactions, which involve the transfer of electrons between atoms.
There are several different methods that can be used to complete equations, including the oxidation number method, the half-reaction method, and the ion-electron method. The oxidation number method is the most straightforward, and it involves assigning oxidation numbers to each atom in the equation.
The half-reaction method is more complex, but it can be used to balance equations that involve complex ions. The ion-electron method is a combination of the oxidation number method and the half-reaction method.
Nuclei Involved, Which nucleus completes the following equation
The nuclei that are involved in equation completion are the atoms that are being oxidized and reduced. The atom that is oxidized is the one that loses electrons, and the atom that is reduced is the one that gains electrons.
The nuclei of the atoms that are being oxidized and reduced are typically metals.
The properties of the nuclei that are involved in equation completion can affect the rate of the reaction. For example, the more reactive a metal is, the more easily it will be oxidized. The more stable a metal is, the more difficult it will be to reduce.
The role of nuclei in chemical reactions is to provide the electrons that are transferred between atoms. The electrons that are transferred are typically from the valence shell of the atom. The valence shell is the outermost shell of electrons in an atom.
Reaction Types
There are several different types of reactions that involve equation completion. The most common type of reaction is a redox reaction, which involves the transfer of electrons between atoms. Other types of reactions that involve equation completion include acid-base reactions, precipitation reactions, and gas-forming reactions.
| Reaction Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Redox reaction | A reaction in which electrons are transferred between atoms. |
| Acid-base reaction | A reaction in which an acid and a base react to form a salt and water. |
| Precipitation reaction | A reaction in which two solutions are mixed and a solid precipitate forms. |
| Gas-forming reaction | A reaction in which a gas is produced. |
The characteristics of each type of reaction can vary depending on the reactants and products involved. For example, redox reactions can be either exothermic or endothermic, while acid-base reactions are typically exothermic.
The factors that affect the type of reaction that occurs include the concentration of the reactants, the temperature, and the presence of a catalyst.
Applications of Equation Completion
Equation completion is a valuable tool that can be used in a variety of applications. Some of the most common applications of equation completion include:
- Predicting the products of a chemical reaction
- Calculating the stoichiometry of a chemical reaction
- Determining the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction
- Solving environmental problems
- Developing new technologies
Equation completion is a powerful tool that can be used to understand and predict the behavior of chemical reactions. It is a valuable tool for chemists and other scientists who work with chemicals.
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of equation completion in chemistry?
Equation completion allows chemists to determine the missing reactants or products in a chemical reaction, providing a deeper understanding of the reaction process and enabling accurate predictions of reaction outcomes.
How does the choice of nucleus affect the completion of an equation?
The properties of the nucleus, such as its atomic number, mass number, and stability, influence the reactivity of the element and its ability to participate in a particular chemical reaction.
What are the different methods used to complete equations?
Common methods include balancing equations, using stoichiometry, and considering the reaction type and the properties of the elements involved.